Bootstrap Columns Group
Introduction
In the previous several years and absolutely the coming ones to come the whole world of internet spread more and even more widely across every type of devices so that currently almost half of the views of the pages on the internet are done not really on personal computer and laptop display screens yet directly from different mobile gadgets along with every types of small-scale display screen dimensions. In this degree assuming that a web page will not show properly-- suggesting to resize and quickly find its own optimal shape on the device applied its generally will get browsed away to get replaced by a mobile phone friendly web page offering identical product or service.
Moreover-- the indexing mechanisms such as Google produce the so called mobile-friendly test and display far down your pages around the search results. This pushing down is even further assuming that the search is made by a mobile machine-- the internet search engines take this particular thing quite seriously. So not possessing a mobile phone friendly page practically points to not having a page anyway.
The way to work with the Bootstrap Columns Grid:
However just what actually a page happening to be responsive suggests-- basically-- fitting all width of the display that gets shown on providing the elements with practical and clear approach at any sizing. To look after this the Bootstrap framework works with so called columns and breakpoints . In a few words the breakpoints are predefined screen widths at which a shift takes place and the Bootstrap Columns jQuery turn reordered to confidently fit preferable. The former version applied 4 breakpoints and the most new Bootstrap 4 framework presents one added so they become actually five. Here they are together with the max value they expand to. The precise boundary number in itself is fitting to the next screen scale.
Extra small up to 34em ( or 544px) – up to Bootstrap 4 Alpha 5 had the -xs- infix. In Bootstrap 4 alpha 6 this infix is dropped so just the number follows;
Small – from 34em up to 48em ( or 768px ) – has the -sm- infix;
Medium – from 48em up to 62em ( or 992px ) – has the -md- infix;
Large – from 62em up to 75em ( 1200px ) - -lg- infix;
Extra large – 75em and everything above it – the new size in Bootstrap 4 – has the -xl- infix.
More suggestions
The horizontal sector in Bootstrap 4 framework gets shared into 12 parts equal in size-- these are the so called columns-- they all hold the .col- prefix. Later comes the display dimension infix which defined down to what display size the column element will span the pointed out quantity of columns. In the case that the display screen size is more compact -- the column feature occupies the full display screen width-- as though it was assigned .col-12 (.col-xs-12 up to Bootstrap 4 alpha 5).
Auto format columns
Employ breakpoint-specific column classes for equal-width columns. Bring in any number of unit-less classes for every breakpoint you need to have and every Bootstrap Columns Table is going to be the same width.
Equal width
As an example, right here are two grid designs that used on each gadget and viewport, from xs.

<div class="container">
<div class="row">
<div class="col">
1 of 2
</div>
<div class="col">
1 of 2
</div>
</div>
<div class="row">
<div class="col">
1 of 3
</div>
<div class="col">
1 of 3
</div>
<div class="col">
1 of 3
</div>
</div>
</div>Putting one column width
Auto-layout for flexbox grid columns also signifies you can establish the width of one column and the others are going to promptly resize about it. You may utilize predefined grid classes ( while demonstrated here), grid mixins, or else inline widths. Note that the various other columns will resize no matter the width of the center column.

<div class="container">
<div class="row">
<div class="col">
1 of 3
</div>
<div class="col-6">
2 of 3 (wider)
</div>
<div class="col">
3 of 3
</div>
</div>
<div class="row">
<div class="col">
1 of 3
</div>
<div class="col-5">
2 of 3 (wider)
</div>
<div class="col">
3 of 3
</div>
</div>
</div>Variable width web content
Employing the col- breakpoint -auto classes, columns can size on its own based upon the regular size of its content. This is super handy having single line web content such as inputs, numbers, and the like. This particular, together with horizontal alignment classes, is very handy for centralizing structures having unequal column sizes as viewport width evolves.
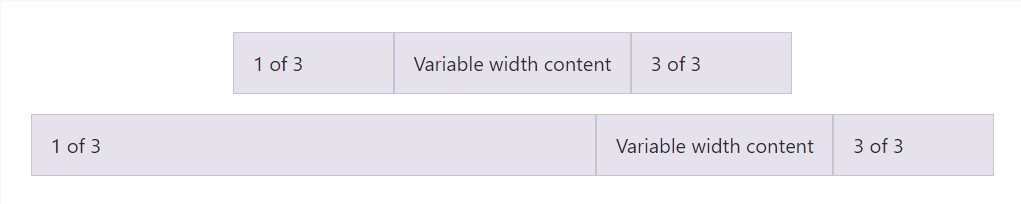
<div class="container">
<div class="row justify-content-md-center">
<div class="col col-lg-2">
1 of 3
</div>
<div class="col-12 col-md-auto">
Variable width content
</div>
<div class="col col-lg-2">
3 of 3
</div>
</div>
<div class="row">
<div class="col">
1 of 3
</div>
<div class="col-12 col-md-auto">
Variable width content
</div>
<div class="col col-lg-2">
3 of 3
</div>
</div>
</div>Identical width multi-row
Build equal-width columns which go across multiple rows through adding a .w-100 just where you desire the columns to break to a new line. Make the breaches responsive via mixing the .w-100 by having some responsive display screen utilities.
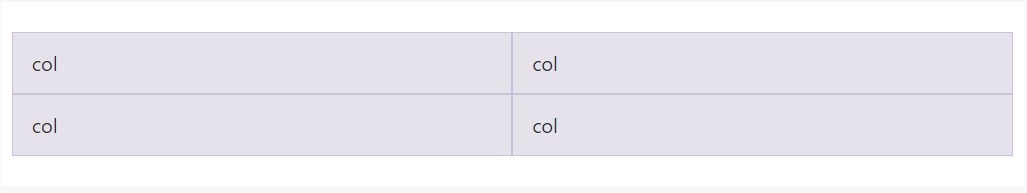
<div class="row">
<div class="col">col</div>
<div class="col">col</div>
<div class="w-100"></div>
<div class="col">col</div>
<div class="col">col</div>
</div>Yet another new feature
Another new thing with the current Alpha 6 build of Bootstrap 4 is on the occasion that you add simply a handful of .col-~ some number here ~ features spanning no more than 12 columns they will really deliver proportionally to have all the area readily available on the row and will certainly continue to be this way at any screen width-- and even under 32em.
Conclusions
And so presently you recognize exactly how the column features form the structure and responsive behavior of the Bootstrap system and all that is certainly left for you is generating something truly fantastic using them.
Inspect some youtube video training regarding Bootstrap columns
Connected topics:
Bootstrap columns authoritative information

Responsive columns in Bootstrap
Problem with a heights of the Bootstrap columns